第12回JMACシンポジウム
「生体模倣システム(MPS)の技術的な発展と標準化における日本の役割」
講演要旨
講演1
MPSの社会実装〜国内外の現状と国際標準化への期待

伊藤 弓弦
筑波大学生命環境系
教授
MPSは、動物実験の代替法として、またヒト生体/器官/組織を生理的に模倣したモデルとして、医薬品開発のみならず化粧品、食品、化学物質のリスク評価等への応用が期待されるプラットフォームであり、日米欧を中心に開発が進んでいる。この技術は微小流路による培養液の灌流を再現するなど、人体を外挿した細胞ベースのアッセイシステムとして期待を集める一方で、解決すべき課題も多い。例えば、COU(Context of Use)に合致した細胞や培養構造の構築、アッセイプロトコールのロバストさ、ユーザビリティーの向上などが大きな技術的な課題としてあげられる。また、システムとして生体模倣系を供給・運用する上で、ハード&ソフトに関わるステークホルダーに求められる専門性も多様であり、そのような背景も社会実装を遅延させる要因の一つとなっている。本発表ではそのような現状をレビューすると共に、その解決を目指した国プロでのアプローチや国際標準化への期待も述べていきたい。
略歴
2001年 東京大学大学院 理学系研究科 博士課程修了
2001年 九州大学大学院 農学研究院 リサーチアソシエイト
2003年 東京大学大学院 21世紀COE 特任研究員
2004年 JST ICORP 器官再生プロジェクト グループリーダー
2007年 東京大学大学院 総合文化研究科 特任助教
2008年 産業技術総合研究所 研究員
2010年 産業技術総合研究所 研究チーム長
2015年 産業技術総合研究所 研究グループ長
2020年 千代田化工建設(株)ライフサイエンス事業部 アソシエイトフェロー(出向元)
2020年 筑波大学 生命環境系 教授(出向先)
現在に至る
講演2
シリコーンゴムを用いたMPSデバイスの作製と応用

三原 将
株式会社朝日FR研究所
主任研究員 博士(工学)
本発表では、シリコーンゴムを用いたMicro Physiological Systems(MPS)デバイスの作製方法とその応用可能性について紹介します。シリコーンゴムは柔軟性・生体適合性に優れており、微細加工技術を用いて精密なチャンネルや構造を形成できることから、MPSデバイスの材料として活用されます。一方で化学的安定性の高さ故に難接着物質であり、一般的な接着剤・両面テープ・熱溶着接着が適用できません。本発表ではシリコーンゴムを様々な基材に接着剤を用いずに接合させる『分子接合技術』及びそれを利用したMPSデバイス作製例をご紹介します。 また、シリコーンゴムは高い透明性と気体透過性を併せ持っており、スフェロイド培養に好適です。シリコーンゴムを超薄膜化させることで更に気体透過性を高め、スフェロイドアレイ培養に適用した例についてもご紹介します。
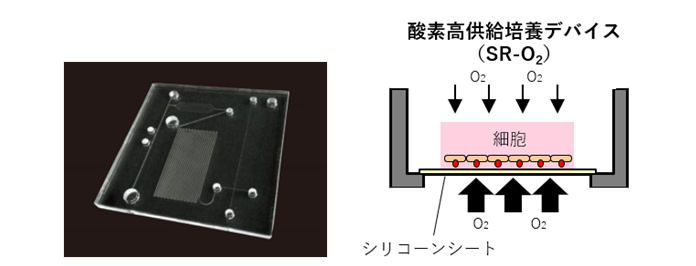
略歴
2012年 株式会社朝日ラバーの研究開発部門である株式会社朝日FR研究所に入社。
2019年 早稲田大学 先進理工学研究科 生命科学専攻 博士後期課程に入学。
2021年 上記大学を卒業し、博士号を取得。
講演3
MPSを用いた創薬支援ツールの開発

三木一郎
株式会社フィジオスバイオテック
代表取締役CEO
製薬や化粧品業界では、動物実験の廃止の流れや、従来法での評価が難しい新規モダリティー (抗体、核酸医薬) の急増などから、従来の研究に加えて、生体模倣システム (MPS)を用いた研究開発の需要が高まっています。しかし、MPSを利用するためには、デバイスの設計、臓器・組織の構築、MPSのハンドリング・計測機器を組合せが必要となり、この構築には幅広い知識と経験を必要とします。 弊社では、京都大学でこれまで培ってきた研究のノウハウを活かし、ユーザーニーズに合わせたMPSの開発・提供を行っています。欧米では、このような総合MPSメーカーが生まれつつありますので、日本発の技術を生かした総合MPSメーカーとなり、世界に進出することを目指しています。そのために、当社は、JMAC MF4MPS専門部会、MPS実用化推進協議会のメンバーとして、標準化に取り組んでいます。
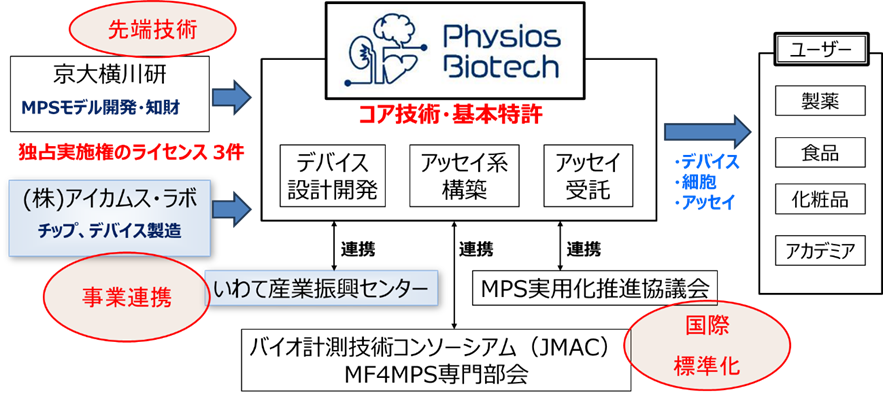
図 株式会社フィジオスバイオテックが目指す総合MPS企業
略歴
協和発酵工業(現協和キリン)でin vitroや細胞を用いたハイスループットスクリーニング、動物を用いた薬理試験、臨床研究、ならびに研究マネージメントに25年間従事。その後、JSTで大学の研究を事業化するプロジェクトおよび、AMEDでVCと連携して創薬スタートアップを育成する事業に従事。理研ならびにディープテックベンチャーで国家プロジェクトのマネージメントを担当。2024年6月より現職。
講演4
MPS技術の国際市場展開と標準化の役割

中江 裕樹
特定非営利活動法人 バイオ計測技術コンソーシアム(JMAC)
事務局長兼研究部長
MPS (Microphysiological System) (もしくはOoC (Organ on a Chip))に関する技術的な発展に伴い、前臨床へのMPSの活用を見据えた国際的な市場にも注目が集まっている。2021年3月にキックオフミーティングを実施し、標準化ニーズについての議論を進めてきたCEN/CENELECのFocus Group (FG)は、本年2024年7月にOoCの標準化ロードマップを出版し、ISOでの標準化に進もうとしている。一方で、MPSデバイスに用いられるMicrofluidics技術については、これまでTC 48/WG 3で集中的に議論されてきた。TC 48はLaboratory Equipmentに関する標準化の専門委員であるが、このTCのWG 3はMicrofluidic deviceに特化した標準化を進めてきており、これまでに4つの規格を出版している。TC 48/WG 3に提案される標準は、MFAという国際協会や、EURAMETという欧州の計量学のプロジェクトのサブプロジェクトであるMFMETにおいて、多くの専門家の意見を集約して開発されてきた。日本は、昨年から、MFAにコンタクトを開始、MFAシンポジウムや、MFMETシンポジウムに参加するのと並行して、それまでオブザーバー(O-メンバー)であったTC 48への参加を積極参加(P-メンバー)に変更して、これらの活動への参加を積極的に進めてきた。日本は、MPSに使われる樹脂材料の評価指標についての標準化を目指して議論を進めてきており、2024年のTC 48のポルトガル会議において、標準化の提案を行い、各国の賛成をいただいてPWI 25486として登録された。本講演では、MPSを取り巻く標準化の状況と、日本の活動について概観する。

略歴
千葉大学理学研究科・生物学専攻卒。博士(理学)。1986年4月、株式会社東芝入社後、1993年学位取得、1994年には、ドイツ・ザールランド大学・医学部へ在職留学。特定非営利活動法人バイオ計測技術コンソーシアム(JMAC)については、設立時より関与し、現在事務局長と研究部長を兼務、さらにISO/TC 34/SC 16/WG 8および、ISO/TC 276/WG 4 のConvenerをはじめ、ISOの専門委員会のエキスパートとしてバイオ分野の標準化を推進している。令和5年度産業標準化事業表彰・経済産業大臣表彰受賞。日本生物資源産業利用協議会(CIBER) 理事。
講演5
Advancing Microfluidics: Standardization Efforts by ISO/TC 48/WG 3 and CEN/TC 332/WG 7

Vania Silverio
INESC MN Microsistemas e Nanotecnologias
Senior Researcher,
Microfluidics Group Leader
ISO/TC 48/WG 3 and CEN/TC 332/WG 7 are working groups focused on the standardization of microfluidics, which involves the manipulation of fluids at a microscale.
ISO/TC 48/WG 3 primarily addresses standardization related to microfluidic devices, including definitions, terminology, and the requirements for design and performance. This group works to establish international standards that ensure interoperability, safety, and quality in microfluidic applications, which can encompass fields such as diagnostics, pharmaceuticals, and environmental monitoring.
CEN/TC 332/WG 7, on the other hand, is focused on standardization within Europe and contributes to the development of European standards for microfluidic systems. This includes guidelines for materials, testing methods, and performance evaluation methods to facilitate market access and compliance across EU member states.
Together, these working groups aim to provide a comprehensive framework for the development, manufacturing, and evaluation of microfluidic technologies, promoting innovation while ensuring safety and reliability in various applications.
略歴
Vania Silverio is a Senior Researcher at INESC MN, leading the Microfluidics Lab. She focuses on innovative solutions that integrate nanotechnology and simulation for designing and testing Microfluidic Platforms, Lab-On-Chip, and Organ-on-Chip systems. Dr. Silverio convenes ISO/TC 48/WG 3 and CEN/TC 332/WG 7 for Microfluidics standardization and is an expert for Organ-on-Chip standards.
She has published extensively in microscale fluid dynamics and microfluidics fabrication, and serves as an Invited Assistant Professor at Instituto Superior Técnico, ULisboa, teaching courses on Microfluidics and Nanofabrication. Silverio is a peer reviewer for scientific journals and actively organizes international meetings in her field. She is a member of several professional organizations, including The Microfluidics Association and the European Organ-on-Chip Society.
Silverio holds a PhD in Mechanical Engineering from Técnico, ULisboa, and a Licenciatura in Technological Chemistry from FCUL, ULisboa.
講演6
Results and impact of MFMET project – establishing metrology standards in microfluidic devices

Elsa Batista
Instituto Português da Qualidade
Head of Volume and Flow Laboratory, Metrology Department
Microfluidics, concerned with fluid-handling in the nano-to-millilitre scale, has major applications in biomedical and chemical analysis however global standards are lacking. ISO/TC48/WG3 has been established to address the standardisation of microfluidic components, interfaces, protocols for associated testing and protocols for microflow control to be applied in the development and the fabrication processes (manufacturing, testing and assembly) of microfluidic devices.
The goal of project MFMET – establishing metrology standards in microfluidic devices is to contribute to the development of globally accepted standards for microfluidic devices and disseminate them to end users in industry, particularly Life Science and Diagnostics Companies, and in academia. This project focus on testing and metrology strategies that are essential to ensure measurement accuracy and traceability of microfluidic devices and will aid product developers in advancing the field of microfluidics. his project developed protocols for measuring different quantities, interface, connectivity, modularity and sensor integration of microfluidic devices based on experimental test results obtained by the new microfluidic transfer standards fabricated by the consortium and literature surveys.
The specific objectives were:
- To investigate, evaluate and formulate consensus-based flow control specifications, guidelines and protocols to enhance the manufacturing capability of the microfluidics industry supply chain through voluntary compliance.
- To develop measurement protocols for different flow quantities and liquid properties, in different microfluidics devices to be used in pharmaceuticals, biomedical and mechanobiology applications. A EURAMET guide and a technical report on these measurement protocols will be developed.
- To define consensus-based standards and guidelines for interfaces and connectivity between fluidic passages and optical/electrical connections of microfluidics components and corresponding measurement standards, from micro to macro size scales.
- To define guidelines for the standardisation of dimensions and accuracy for modularity (either module-to-module or module-to-world) and sensor integration (combination of sensing elements/materials with microfluidic modules), in accordance with good practices in microfluidic component design and manufacturing.
- To collaborate with ISO/TC48/WG3 and end users of the standards (e.g. health and pharmaceutical industry) to ensure that the outputs of the project are aligned with their needs and in a form that can be incorporated into standards (e.g. new technical guides, ISO 10991 and ISO/CD 22916) at the earliest opportunity.
In general, the project supported several ISO technical committees in the development and revision of standards related to microfluidic technology by incorporating the results obtained in the different activities of the project. It also contributed to the developed of roadmaps of ISO TC 48 and FGOOC. Several workshops for industry and academia and metrologist were performed with very good feedback from all of the attendees. A microfluidic components database was produced and a webinar on metrology standards for microfluidics was developed. All this information has been very well accepted by the microfluidic community and this can be observed by the more than 2500 downloads of documents on the project’s Zenodo website.
This presentation will detail the state of the art, the underlying needs, the objectives, the impact and results of project MFMET (figure 1 and figure 2) .

Figure 1. Burst pressure setup with microfluidic chip at CETIAT.
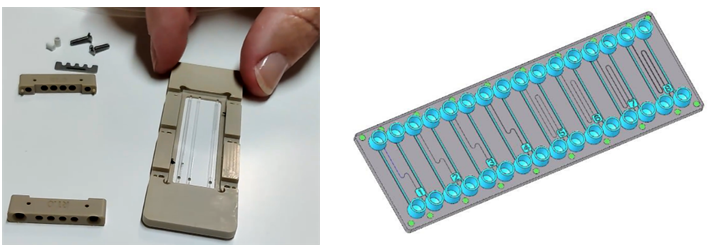
Figure 2. Transfer standards, on the left the glass chip and on the right the polymer chip.
略歴
Has a PhD in Mechanical Engineering from Universidade Nova de Lisboa / Faculty of Sciences (FCT/UNL).
She is the responsible for the Volume and Flow Laboratory of the Portuguese Institute for Quality (IPQ) since 2002. Having started working at IPQ in 1999.
She is the convenor of the Volume subgroup of EURAMET technical committee and the Portuguese contact person for this committee.
Member of several international standardization technical committees, ISO TC 48, ISO TC28 and ISO TC84 and won the CEN-CENELEC Standards + Innovation Awards 2023 for the individual researcher category.
She has several articles published in national and international magazines in the scope of volume and flow metrology, one of this paper was recently was linked to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, helping to tackle some of the world’s greatest challenges.
She participated in the development of several national and international guides, namely: EURAMET cg 21 cg 19, cg 27 in the area of volume and flow metrology.
She was the coordinator of the EURAMET international project “MeDDII – Metrology for drug delivery II” and “MFMET – Establishing metrology standards in microfluidic devices”.








